Step-by-Step Guide to Industrial FDM Printing in Chicago: From Design to Production
Introduction to Industrial FDM Printing
As the heart of America’s manufacturing sector, Chicago is a bustling hub for industrial advancements, including Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) 3D printing. This innovative technology is transforming the production landscape, offering businesses a powerful tool for creating precise and durable parts. In this guide, we will explore the step-by-step process of industrial FDM printing, from initial design to final production.
Understanding FDM Technology
FDM is a popular 3D printing method that uses a continuous filament of thermoplastic material to construct parts layer by layer. The process involves extruding the material through a heated nozzle, allowing it to be deposited precisely where needed. This technique is particularly valued for its ability to produce strong, lightweight components suitable for various industrial applications.

Step 1: Designing Your Model
The first step in the FDM printing process is designing your model using Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software. This digital blueprint outlines every detail of the part you wish to produce. It is crucial to ensure that your design is optimized for FDM printing, considering factors such as overhangs, support structures, and material shrinkage.
Choosing the Right Software
Several CAD software options are available, each with unique features and capabilities. Selecting the right tool depends on the complexity of your project and the specific requirements of your industry. Popular choices include SolidWorks, AutoCAD, and Fusion 360, all offering robust tools for creating detailed and precise designs.
Step 2: Preparing for Printing
Once your design is complete, the next step involves preparing your model for printing. This includes converting your design into a format that the printer can understand, typically using slicing software. This software divides the model into thin layers and generates a G-code file that instructs the printer on how to build each layer.

Selecting the Appropriate Material
Choosing the right filament material is critical to achieving the desired properties of your printed part. Common materials include ABS, PLA, and nylon, each offering different advantages in terms of strength, flexibility, and thermal resistance. It is essential to select a material that aligns with your part’s functional requirements.
Step 3: The Printing Process
With your design and materials prepared, it’s time to move on to the actual printing process. The FDM printer will follow the instructions from the G-code file, carefully depositing each layer of material. This stage requires monitoring to ensure optimal print quality and address any issues that may arise during production.
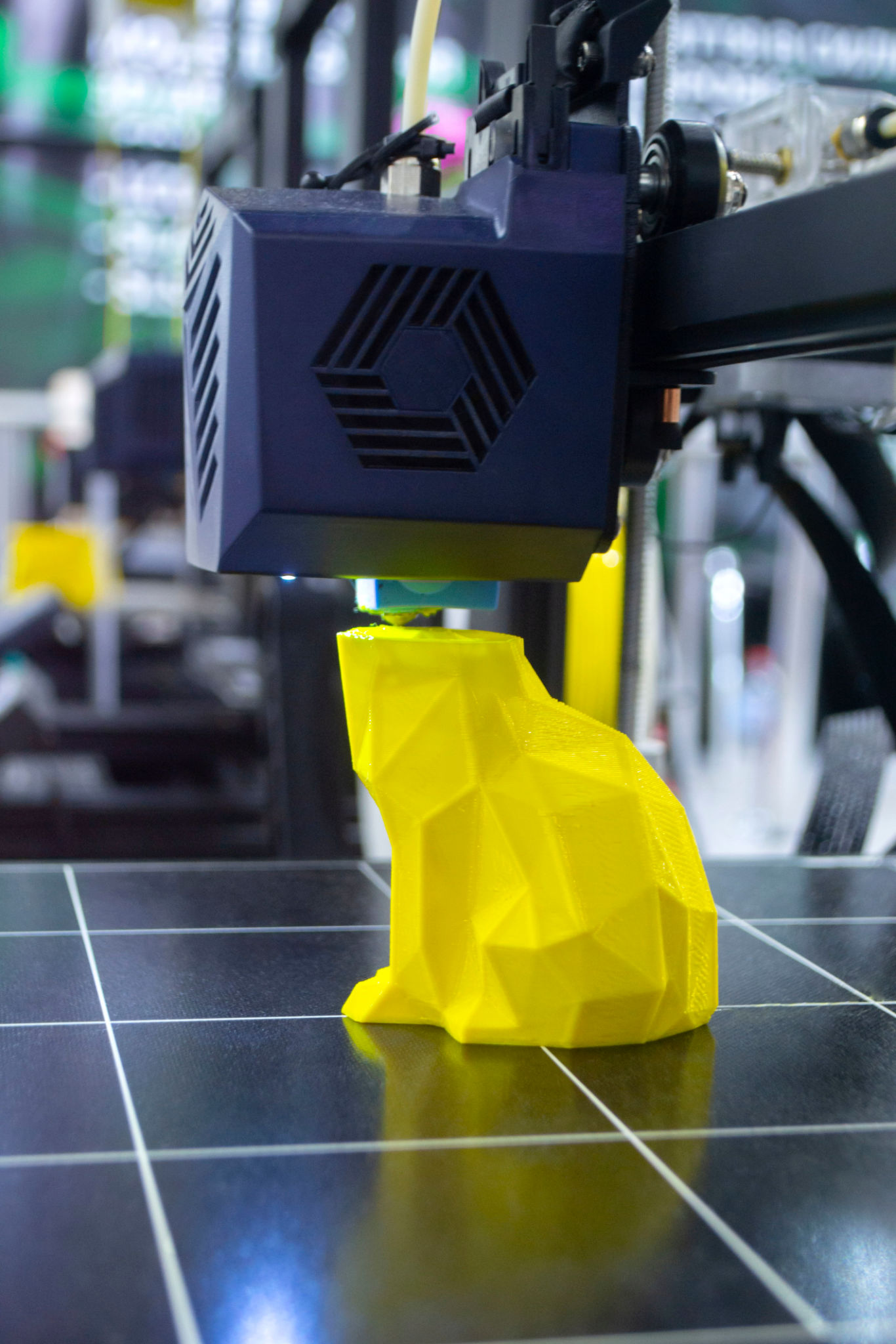
Post-Processing and Quality Control
After printing, parts often require post-processing to achieve a smooth finish or enhance specific properties. This may involve sanding, painting, or applying chemical treatments. Quality control is also a critical step, where you must inspect the parts for accuracy and consistency against the original design specifications.
Step 4: Final Production and Application
Once post-processing is complete, your FDM-printed parts are ready for final application. In Chicago’s diverse industrial sectors, these parts find uses in automotive, aerospace, medical devices, and consumer products, demonstrating the versatility and efficiency of FDM technology in modern manufacturing.
By following this step-by-step guide to industrial FDM printing in Chicago, businesses can harness this cutting-edge technology to streamline production processes and enhance product innovation. Whether you're new to 3D printing or looking to refine your approach, understanding each stage of this process is key to achieving outstanding results.